Labrum Tears – Symptoms and Causes
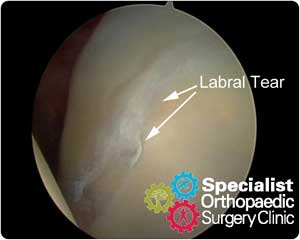
Diagnosing a labrum tear is basically a combination of x-rays, a physical exam and possibly an MRI or arthroscopic test
In order for a diagnosis to be made, there needs to be signs of the torn labrum and at the very least, there must be symptoms that occur before or after the tear has occurred. Treatment for this condition usually depends on location, type and severity of the torn labrum.
Labrum tears are common, particularly in athletes and those with a history of high impact sports such as basketball, football and tennis. Some people also experience labrum tears during or after an injury they sustained, usually to the same area of their shoulder. When tears occur in the tendon and tendons near the top of the shoulder, these are known as bursitis.
Bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa, which is a sack-like structure that lubricates the interior of the shoulder joint. The bursa functions as a lubricant that helps protect the tendon capsule from friction that causes pain, inflammation and other symptoms of bursitis. Sometimes, when bursitis is caused by an injury, it may extend to the bursa leading to bursitis, but it is generally more common to cause bursitis after an injury to the muscle itself. This type of bursitis is referred to as subacromial bursitis.
There are a number of conditions that can contribute to or worsen the symptoms of a labrum tear, such as bursitis. Often times, the symptoms will go away as quickly as they started. If left unchecked, however, the symptoms can become more serious. These complications are sometimes related to a more serious underlying condition or injury.
The most common symptoms of labrum tears are pain, stiffness, instability. Some of the more severe symptoms include tightness, pain and swelling in the shoulder and arm. Most of these symptoms can often be easily detected on the x-ray.
However, due to the nature of these symptoms, they are difficult to diagnose and may go away on their own. Often, a diagnosis is made only after an arthroscope, which is an instrument that can be used to view the bursa under a small telescope, is used to see if there is damage to the bursa.
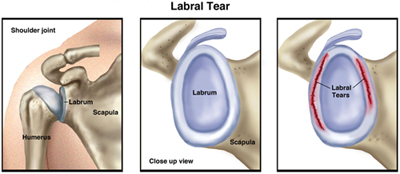
As soon as damage to the bursa is found, the doctor may recommend surgery to remove it. Surgery is not always necessary, but if necessary, it will involve both removal and suturing. In addition to the bursa, if the bursa is in the cuff, some of the supporting tissue can also be removed to heal and repair the injury.
If the bursa is not in the cuff, it can be treated with physical therapy. Physical therapy can help the bursa heal and restore its function. If the bursa cannot heal on its own, surgery may be recommended, but some form of tape will likely need to be inserted to support the bursa.
Symptoms of a ruptured upper lip cannot be ignored. Pain, weakness, and difficulty moving an arm or shoulder may be signs that the bursa is causing pain. These symptoms can be quite unpleasant and cannot be ignored.
In addition to the symptoms described above, if the pain continues for a longer period of time, it is important to see a doctor to determine the cause of the pain. Sometimes this type of bursitis is caused by trauma, which can be treated with adequate rest and proper rehabilitation.
If the bursa is causing the pain, surgery may be recommended in order to relieve the bursa and the inflammation. If the bursa is injured due to a torn muscle, then surgery may be recommended to correct the problem. If the bursa is injured due to other health issues, such as arthritis, surgery may be recommended as a way to relieve the pain and reduce the severity of the bursitis.
Finally, the surgeon may recommend anti-inflammatory medications and/or other treatment options to prevent further symptoms from occurring. These types of treatment options may include physical therapy, surgery, or surgery if the bursa is inflamed and cannot heal on its own.